-
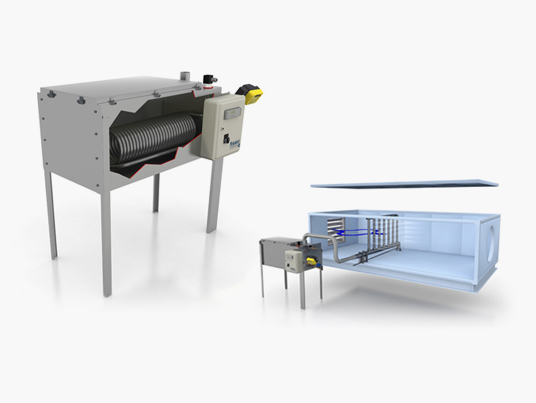
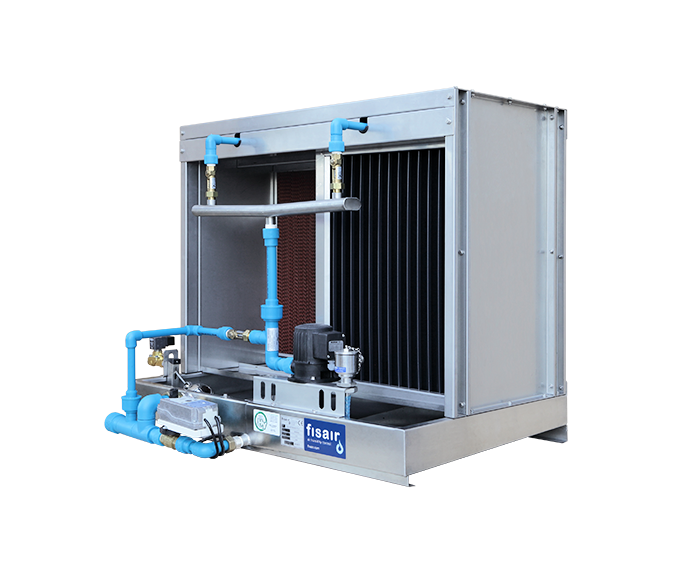 The most hygienic and efficient.Contact panel evaporative humidifiers, with the best performance on the market for efficiency at lower pressure drop and certified hygiene.
The most hygienic and efficient.Contact panel evaporative humidifiers, with the best performance on the market for efficiency at lower pressure drop and certified hygiene. -
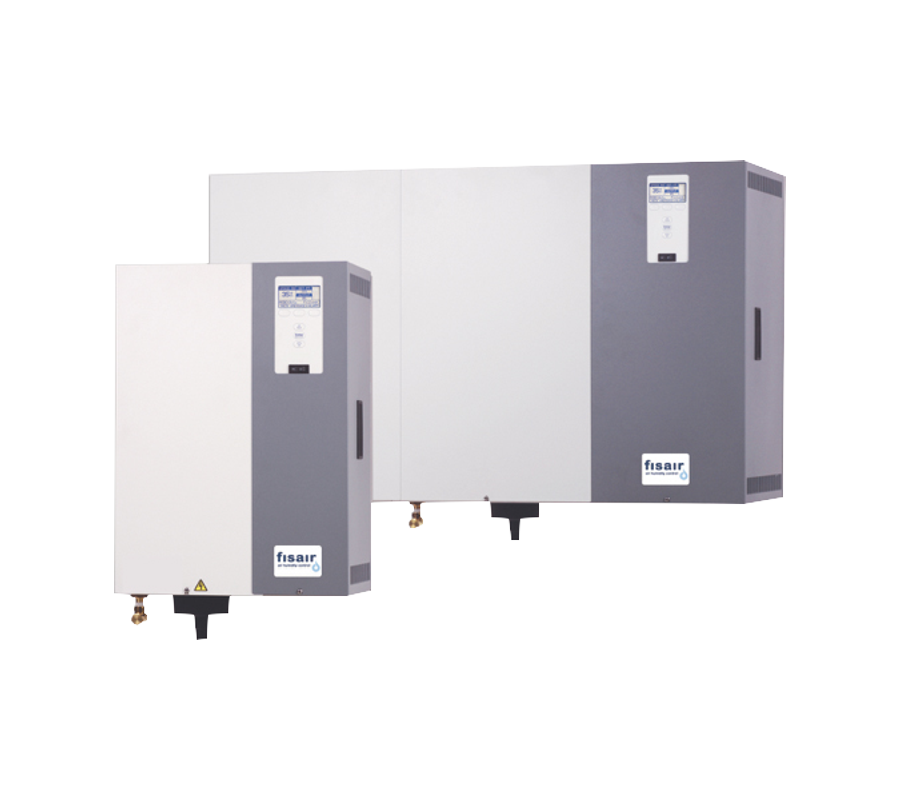 Isothermal self-producer steam humidifiers by submerged electrodes; resistant, compact, economic and precise. It has a stainless steel chassis, controller and wide selection of dispersion systems in accordance with the absorption distance.
Isothermal self-producer steam humidifiers by submerged electrodes; resistant, compact, economic and precise. It has a stainless steel chassis, controller and wide selection of dispersion systems in accordance with the absorption distance. -
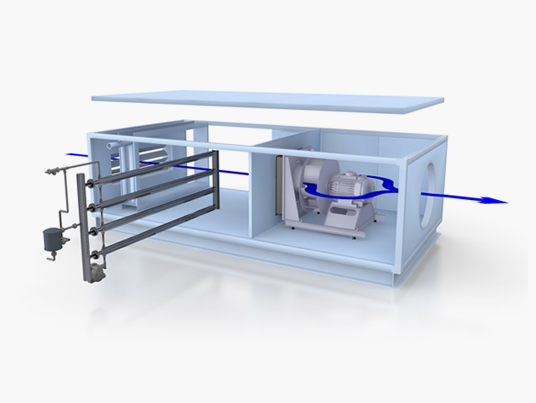 Steam injection humidifiers system designed for work with pressurized boiler steam, with double jacketed piping and steam separator. Air humidification systems.
Steam injection humidifiers system designed for work with pressurized boiler steam, with double jacketed piping and steam separator. Air humidification systems. -
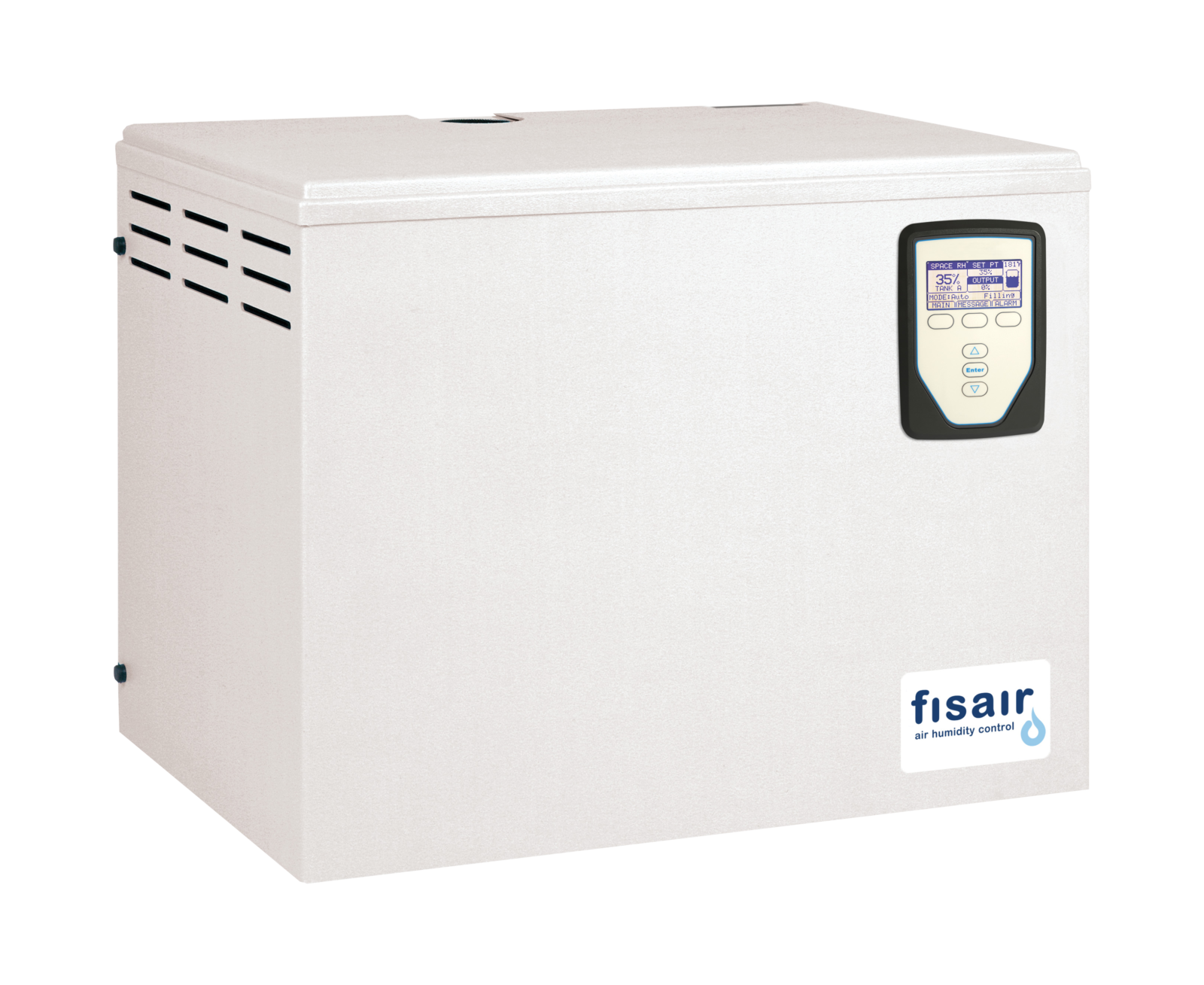 Electric heater isothermal sefl-generating steam humidifiers. Similar to the electrode option but used for any supply water quality. Proportional control.
Electric heater isothermal sefl-generating steam humidifiers. Similar to the electrode option but used for any supply water quality. Proportional control. -
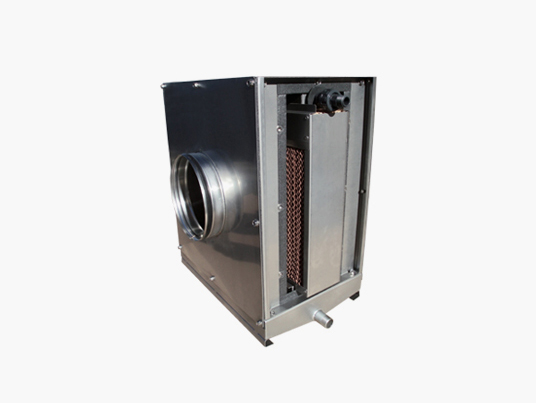 Low height solution The hygienic range for reduced heights enables the use of these systems in false ceilings in commercial premises or offices.
Low height solution The hygienic range for reduced heights enables the use of these systems in false ceilings in commercial premises or offices. -
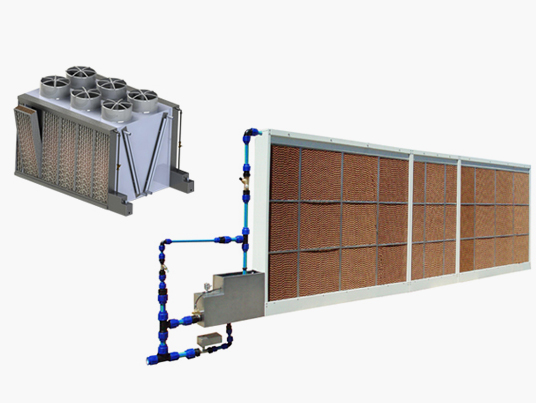 Most hygienic and efficient. Contact panel evaporative humidifiers, with the best performance on the market for lower pressure drop efficiency and certified hygiene. Contact panel evaporative humidifiers, with the best performance in the market for lower pressure drop efficiency and certified hygiene.
Most hygienic and efficient. Contact panel evaporative humidifiers, with the best performance on the market for lower pressure drop efficiency and certified hygiene. Contact panel evaporative humidifiers, with the best performance in the market for lower pressure drop efficiency and certified hygiene. -
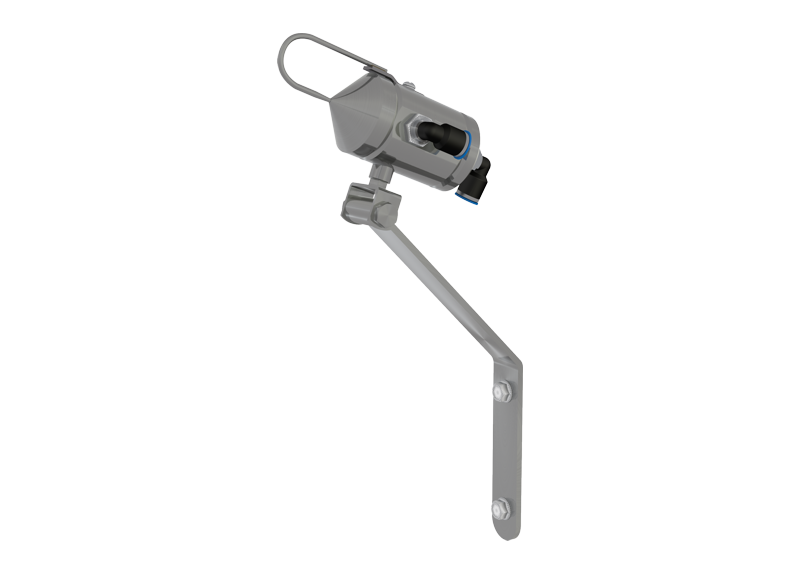
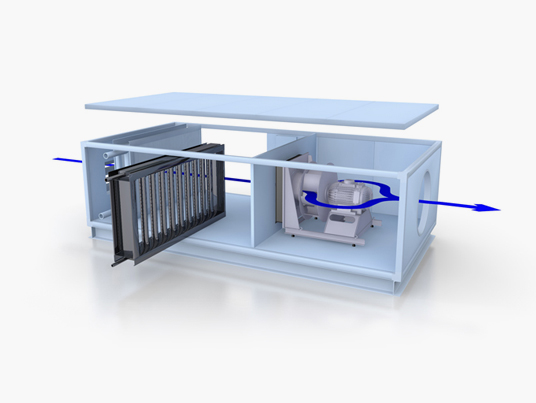 Steam injection/dispersion system for working with pressurised boiler steam or unpressurised steam generated by isothermal steam humidifiers.
Steam injection/dispersion system for working with pressurised boiler steam or unpressurised steam generated by isothermal steam humidifiers.
In commercial buildings such as hotels, offices, etc. and cultural buildings like cinemas, theaters, etc., among many others, a relative humidity of between 40 and 60%RH is considered optimal.
Various studies recommend these limits for the comfort, health and general wellbeing of their inhabitants, prevention of static electricity and longevity of buildings


 Human resistance to infection is reduced when extremes of moisture occur. At low humidity the usually protective nasal mucous membranes in the nose and upper respiratory tract dry out, exposing the living skin to direct contact with infectious organisms. Conversely, when the humidity is high, fungi can grow, releasing volatile, odorous, organic gases.
Human resistance to infection is reduced when extremes of moisture occur. At low humidity the usually protective nasal mucous membranes in the nose and upper respiratory tract dry out, exposing the living skin to direct contact with infectious organisms. Conversely, when the humidity is high, fungi can grow, releasing volatile, odorous, organic gases.
 When friction occurs between two surfaces, there will be an electrical load from the surface atoms stored on both surfaces, creating a potential difference. Most of the time, when both surfaces are connected to ground, these electrical loads discharge quickly, however, if the electrical resistance of the materials is high, sometimes this load will be released, or discharged, on another surface of lower electrical resistance. This discharge is known as an electrostatic energy discharge.
When friction occurs between two surfaces, there will be an electrical load from the surface atoms stored on both surfaces, creating a potential difference. Most of the time, when both surfaces are connected to ground, these electrical loads discharge quickly, however, if the electrical resistance of the materials is high, sometimes this load will be released, or discharged, on another surface of lower electrical resistance. This discharge is known as an electrostatic energy discharge. Our bodies cool down by dissipating heat that causes sweat to evaporate. At 21°C in winter we can be cold because we evaporate too much, due to low relative humidity. At 23°C in summer we can be hot even in light clothing because we do not manage to evaporate sweat, due to high relative humidity in the environment.
Our bodies cool down by dissipating heat that causes sweat to evaporate. At 21°C in winter we can be cold because we evaporate too much, due to low relative humidity. At 23°C in summer we can be hot even in light clothing because we do not manage to evaporate sweat, due to high relative humidity in the environment.